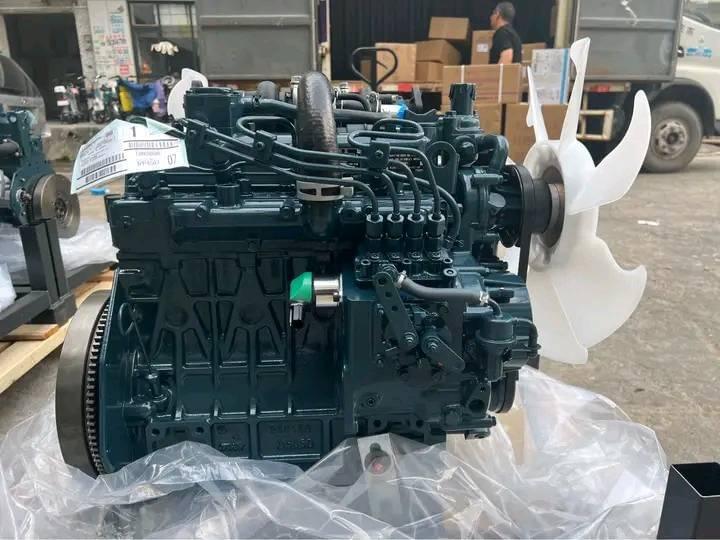
Heavy machinery operators and fleet managers understand that maintaining optimal excavator engine performance is crucial for project success and operational efficiency. When an excavator engine experiences issues, it can lead to costly downtime, delayed project timelines, and significant repair expenses. Understanding the most common problems that affect excavator engines and their corresponding solutions enables operators to implement preventive measures and address issues before they escalate into major failures.
Modern excavator engines are sophisticated powerplants that operate under extreme conditions, including high temperatures, heavy loads, and continuous operation cycles. These demanding environments make excavator engines susceptible to various mechanical and operational challenges that require prompt attention and proper maintenance protocols. Professional technicians and equipment operators must recognize early warning signs and implement systematic troubleshooting approaches to maintain peak performance levels.
Primary Engine Performance Issues
Power Loss and Reduced Performance
Power loss represents one of the most frequently reported excavator engine problems, manifesting as reduced hydraulic system performance, slower operational speeds, and inability to handle normal workloads. This condition typically develops gradually, making early detection challenging for operators who may adapt their working patterns to compensate for declining performance. Several underlying factors contribute to power loss, including fuel system contamination, air intake restrictions, and internal engine wear that affects compression ratios.
Fuel system contamination often occurs when water, dirt, or other particles enter the fuel tank through inadequate filtration or compromised fuel storage practices. Contaminated fuel affects combustion efficiency and can damage sensitive injection system components, leading to irregular fuel delivery and reduced power output. Regular fuel quality testing and proper filtration system maintenance help prevent these issues from developing into costly repairs.
Overheating and Temperature Control
Temperature-related problems in excavator engines can cause severe damage if not addressed promptly, as excessive heat affects metal components, seals, and lubricating oil properties. Overheating typically results from cooling system malfunctions, including radiator blockages, coolant leaks, or thermostat failures that disrupt normal heat dissipation processes. Environmental factors such as high ambient temperatures and heavy dust conditions can exacerbate cooling system challenges.
Cooling system maintenance requires regular inspection of radiator fins, coolant levels, and circulation pump operation to ensure optimal heat transfer capabilities. Blocked radiator cores prevent adequate airflow, while low coolant levels reduce the system's ability to absorb and dissipate engine heat effectively. Professional maintenance schedules should include cooling system pressure testing and coolant quality analysis to identify potential problems before they cause engine damage.
Fuel System Complications
Injection System Malfunctions
Modern excavator engines rely on precision fuel injection systems that deliver exact amounts of fuel at specific timing intervals to optimize combustion efficiency and emissions control. Injection system problems can manifest as rough idling, black smoke emissions, reduced fuel economy, and irregular engine operation that affects overall machine performance. Common injection system issues include worn injector nozzles, contaminated fuel, and electronic control system malfunctions.
Fuel injector wear occurs naturally over time as high-pressure fuel flow erodes internal components, but contaminated fuel accelerates this degradation process significantly. Water in fuel systems can cause corrosion damage to precision-machined surfaces, while particulate contamination can clog small passages and affect spray patterns. Regular fuel filter replacement and fuel system cleaning help maintain injection system integrity and prevent costly component failures.
Fuel Quality and Contamination Issues
Poor fuel quality represents a significant threat to excavator engine reliability and longevity, as contaminated or degraded fuel affects combustion characteristics and can damage sensitive system components. Fuel contamination sources include water infiltration, microbial growth, particulate matter, and chemical degradation that occurs during extended storage periods. These contaminants can cause injection system damage, fuel pump wear, and combustion irregularities that reduce engine performance.
Water contamination poses particular risks to excavator engine fuel systems because water promotes corrosion, supports microbial growth, and can freeze in cold conditions, blocking fuel lines and filters. Implementing proper fuel storage practices, including regular tank drainage and water separation, helps maintain fuel quality and prevent contamination-related problems. Fuel additives and biocides may be necessary in certain operating environments to prevent microbial growth and fuel degradation.
Lubrication and Oil Management
Oil Pressure and Circulation Problems
Adequate oil pressure and circulation are essential for excavator engine protection, as lubricating oil reduces friction between moving parts, carries away heat, and helps seal combustion chambers. Oil pressure problems can indicate worn oil pumps, clogged oil passages, or excessive internal engine wear that allows pressure to bypass normal circulation paths. Low oil pressure conditions can cause rapid engine damage, making early detection and correction critical for preventing catastrophic failures.
Oil circulation system maintenance involves regular pressure testing, oil quality analysis, and filter replacement to ensure proper lubrication reaches all engine components. Worn bearings, damaged seals, and clogged oil galleries can disrupt normal circulation patterns and create localized lubrication failures. Professional diagnostic equipment can identify circulation problems before they cause permanent engine damage, enabling proactive maintenance interventions.
Oil Contamination and Degradation
Engine oil quality directly affects excavator engine performance and component longevity, as contaminated or degraded oil loses its protective properties and may actually accelerate wear processes. Oil contamination sources include combustion byproducts, external dirt infiltration, coolant leaks, and fuel dilution that change oil viscosity and chemical properties. Regular oil analysis programs help identify contamination trends and determine optimal oil change intervals based on actual operating conditions.
Excavator engines operating in dusty environments face increased oil contamination risks from airborne particles that enter through breather systems and worn seals. Implementing effective air filtration systems and maintaining proper breather system operation helps minimize external contamination. Extended oil change intervals may be appropriate in clean operating environments, while severe duty applications require more frequent oil changes to maintain adequate protection levels.
Air Intake and Filtration Challenges
Air Filter Maintenance and Replacement
Clean air intake is fundamental to excavator engine performance and longevity, as contaminated air can cause rapid cylinder wear, reduced power output, and premature component failure. Air filtration systems must remove particles while maintaining adequate airflow for combustion requirements, creating a balance between filtration efficiency and restriction levels. Clogged air filters reduce available airflow and can cause the engine to run rich, while damaged filters allow contaminants to enter the combustion chamber.
Excavator engines operating in construction environments face extreme air contamination challenges from dust, debris, and other airborne particles that can quickly overwhelm filtration systems. Implementing proper filter maintenance schedules based on operating conditions rather than fixed time intervals helps optimize filtration performance. Pre-cleaners and enhanced filtration systems may be necessary for severe dust conditions to extend filter life and improve protection levels.
Turbocharger and Boost Pressure Issues
Turbocharged excavator engines depend on proper boost pressure levels to maintain rated power output and fuel efficiency, making turbocharger system health critical for overall engine performance. Turbocharger problems can manifest as reduced power, excessive smoke, unusual noises, and altered boost pressure readings that indicate internal component wear or system restrictions. Common turbocharger issues include bearing wear, compressor wheel damage, and wastegate malfunctions that affect boost control.
Turbocharger maintenance requires attention to oil quality, air filtration, and operating procedures that affect component longevity. Contaminated oil can damage precision turbocharger bearings, while poor air filtration allows abrasive particles to erode compressor and turbine wheels. Proper engine warm-up and cool-down procedures help extend turbocharger life by preventing thermal shock and ensuring adequate lubrication during critical operating phases.
Electronic Control System Issues
Sensor Failures and Diagnostic Codes
Modern excavator engines incorporate sophisticated electronic control systems that monitor operating parameters and adjust fuel delivery, timing, and emissions control systems for optimal performance. Electronic system failures can cause various operational problems, including reduced power, increased emissions, and protection system activation that limits engine operation. Diagnostic trouble codes provide valuable information for troubleshooting electronic system problems and identifying specific component failures.
Sensor failures represent common electronic system problems that can affect engine performance and emissions compliance, as faulty sensors provide incorrect information to control modules. Temperature sensors, pressure sensors, and position sensors must operate within specified parameters to ensure proper system function. Regular diagnostic system testing and sensor calibration help maintain electronic system reliability and prevent performance problems related to sensor drift or failure.
Wiring and Connection Problems
Electrical connections and wiring harnesses in excavator engines face challenging operating conditions, including vibration, temperature extremes, and moisture exposure that can cause connection failures and signal interference. Corroded connections, damaged wiring, and loose terminals can create intermittent problems that are difficult to diagnose and may cause erratic engine behavior. Implementing proper wiring protection and connection maintenance helps prevent electrical system problems.
Environmental protection for electrical components becomes critical in excavator applications where exposure to water, chemicals, and abrasive materials can damage sensitive electronic systems. Sealed connections, proper routing, and regular inspection help maintain electrical system integrity. Professional diagnostic equipment can identify electrical problems before they cause system failures, enabling proactive maintenance interventions that prevent costly downtime.
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Regular Inspection Protocols
Systematic inspection protocols form the foundation of effective excavator engine maintenance programs, enabling early problem detection and preventing minor issues from developing into major failures. Daily, weekly, and periodic inspection schedules should address fluid levels, visual condition assessments, and operational parameter monitoring that provides insight into engine health. Documenting inspection results creates valuable maintenance history records that help identify developing trends and optimize maintenance intervals.
Professional maintenance programs incorporate condition monitoring techniques such as oil analysis, vibration monitoring, and thermal imaging that provide objective data about engine condition. These diagnostic tools can identify internal wear patterns, lubrication problems, and developing mechanical issues before they cause operational problems. Trending analysis helps predict maintenance needs and optimize component replacement timing based on actual condition rather than arbitrary time intervals.
Fluid Analysis and Monitoring
Regular fluid analysis programs provide valuable insights into excavator engine condition and help optimize maintenance schedules based on actual operating conditions rather than generic recommendations. Oil analysis can detect internal wear metals, contamination levels, and additive depletion that indicate developing problems or maintenance needs. Coolant analysis helps identify system leaks, corrosion issues, and chemical balance problems that affect cooling system performance and component longevity.
Fuel analysis becomes particularly important for excavator engines operating in remote locations or using fuel from multiple sources, as fuel quality variations can affect engine performance and component life. Water content, particulate contamination, and chemical properties should be monitored to ensure fuel meets engine manufacturer specifications. Implementing fuel testing protocols helps prevent contamination-related problems and optimizes fuel system maintenance intervals.
Troubleshooting and Diagnostic Approaches
Systematic Problem Identification
Effective troubleshooting requires systematic approaches that eliminate variables and focus diagnostic efforts on the most likely problem areas based on symptoms and operating history. Professional diagnostic procedures typically begin with operational tests, visual inspections, and basic parameter measurements before proceeding to more complex testing procedures. Documenting symptoms, operating conditions, and recent maintenance activities helps narrow diagnostic focus and avoid unnecessary testing.
Modern excavator engines incorporate sophisticated diagnostic capabilities that provide valuable troubleshooting information through electronic control systems and monitoring equipment. Diagnostic trouble codes, parameter displays, and data logging capabilities help identify system problems and monitor repair effectiveness. Professional diagnostic equipment can access detailed system information that enables precise problem identification and verification of repair procedures.
Professional Diagnostic Equipment
Advanced diagnostic equipment enables precise excavator engine problem identification and helps optimize repair procedures for maximum effectiveness and reliability. Electronic diagnostic tools can access control system parameters, retrieve historical data, and perform specialized tests that identify intermittent problems or developing issues. Pressure testing equipment, flow meters, and thermal measurement devices provide objective data about system performance and component condition.
Investment in quality diagnostic equipment pays dividends through reduced diagnostic time, improved repair accuracy, and enhanced preventive maintenance capabilities. Professional-grade equipment often includes software updates and technical support that keep pace with evolving engine technologies and diagnostic procedures. Training programs help technicians maximize diagnostic equipment capabilities and stay current with changing troubleshooting techniques and repair procedures.
FAQ
How often should excavator engine oil be changed
Excavator engine oil change intervals depend on operating conditions, engine design, and oil quality, but typically range from 250 to 500 operating hours. Severe duty applications including dusty environments, extreme temperatures, or continuous operation may require more frequent changes. Oil analysis programs help determine optimal change intervals based on actual oil condition rather than arbitrary time periods, potentially extending intervals in favorable conditions while ensuring adequate protection in demanding applications.
What causes excessive black smoke from excavator engines
Black smoke from excavator engines typically indicates incomplete fuel combustion caused by factors such as clogged air filters, worn fuel injectors, improper fuel timing, or overloading conditions. Air restriction problems prevent adequate oxygen supply for complete combustion, while fuel system issues can cause excessive fuel delivery or poor spray patterns. Turbocharger problems may also contribute to black smoke by reducing combustion air pressure and disrupting the air-fuel mixture balance.
Why does my excavator engine lose power during operation
Power loss during excavator engine operation can result from fuel system problems, air intake restrictions, cooling system issues, or internal engine wear that affects compression. Contaminated fuel filters, clogged air cleaners, or overheating conditions commonly cause gradual power loss. Electronic system problems including sensor failures or control module issues may also limit engine power output as protection measures. Systematic diagnosis helps identify the specific cause and determine appropriate repair procedures.
How can I prevent excavator engine overheating problems
Preventing excavator engine overheating requires regular cooling system maintenance including radiator cleaning, coolant level checks, and thermostat testing to ensure proper heat dissipation. Clean radiator cores and adequate airflow are essential for heat transfer, while proper coolant mixture ratios provide optimal heat absorption and freeze protection. Regular cooling system pressure testing helps identify leaks before they cause overheating, and temperature monitoring systems provide early warning of developing problems.

