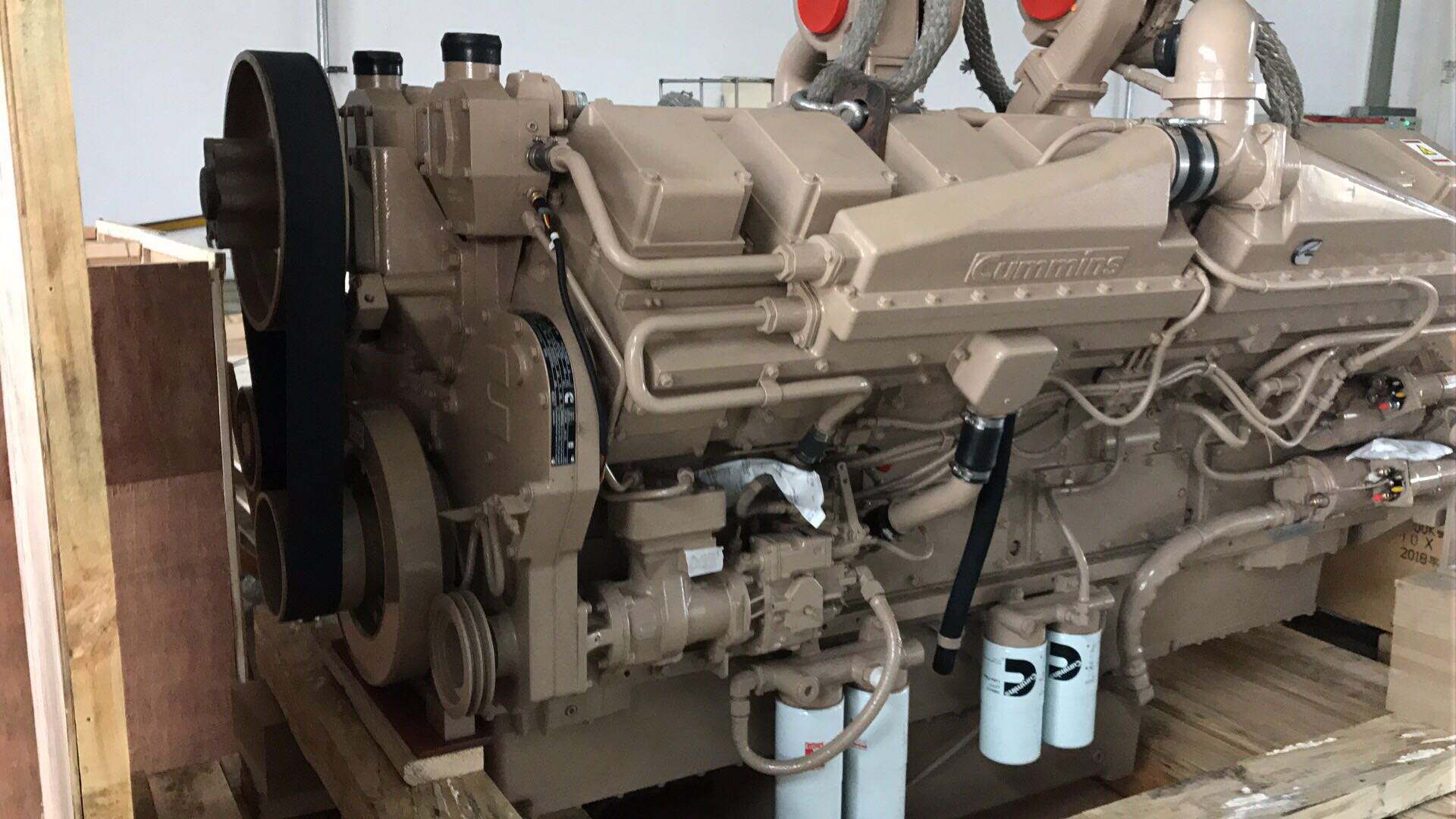
Proper maintenance is the cornerstone of extending the service life and ensuring optimal performance of your cummins engine. Whether powering marine vessels, trucks, or heavy machinery, these robust diesel engines demand systematic care to deliver reliable operation across thousands of hours. Understanding the essential maintenance procedures, recognizing early warning signs of potential issues, and implementing preventive measures can significantly reduce downtime and repair costs. This comprehensive guide provides expert insights into maintaining your cummins engine for maximum efficiency and longevity.

Essential Routine Maintenance Procedures
Oil Change Intervals and Specifications
Regular oil changes form the foundation of cummins engine maintenance protocols. The recommended oil change interval typically ranges from 250 to 500 hours of operation, depending on operating conditions and engine model specifications. Severe duty applications such as marine environments or dusty construction sites may require more frequent oil changes to prevent contamination buildup. Always use manufacturer-approved oil grades that meet API specifications and viscosity requirements for your specific engine model.
When performing oil changes, inspect the oil filter condition and replace it simultaneously with fresh oil. The oil filter removes contaminants that could damage internal engine components, making its replacement crucial for maintaining engine health. Check oil levels regularly between scheduled changes, as consistent monitoring helps identify potential leaks or excessive consumption issues before they escalate into major problems.
Air Filter Maintenance and Replacement
The air filtration system plays a critical role in protecting your cummins engine from harmful particulates that could cause premature wear. Inspect air filters every 100 hours of operation or more frequently in dusty environments. A clogged air filter restricts airflow, reducing engine power and increasing fuel consumption while potentially allowing contaminants to enter the combustion chamber.
Replace air filters when they show visible contamination or when restriction indicators reach specified limits. Some applications benefit from pre-cleaners or upgraded filtration systems that extend filter life and provide enhanced protection. Never operate the engine without proper air filtration, as even brief exposure to unfiltered air can cause significant internal damage requiring costly repairs.
Cooling System Maintenance Strategies
Coolant System Inspection and Service
Maintaining proper cooling system function prevents overheating and extends cummins engine component life significantly. Inspect coolant levels weekly and monitor for leaks around hoses, connections, and the radiator. The coolant mixture should maintain proper freeze protection and corrosion inhibition according to manufacturer specifications, typically requiring a 50/50 mixture of antifreeze and distilled water.
Replace coolant according to the maintenance schedule, usually every 2000 hours or annually, whichever occurs first. Flush the cooling system completely during coolant changes to remove accumulated deposits and contaminants. Test coolant quality regularly using test strips or refractometers to ensure adequate protection levels are maintained throughout the service interval.
Radiator and Heat Exchanger Care
Clean radiator fins and heat exchanger surfaces regularly to maintain efficient heat transfer capabilities. Accumulated debris, dirt, and marine growth can significantly reduce cooling efficiency, leading to elevated operating temperatures. Use compressed air or low-pressure water to remove surface contamination, working from the clean side outward to avoid pushing debris deeper into the cooling passages.
Inspect radiator cores for damage, corrosion, or leaks that could compromise cooling system integrity. Marine applications require additional attention to saltwater corrosion and marine growth that can block cooling passages. Consider installing sacrificial anodes in marine cooling systems to provide additional corrosion protection for engine components exposed to seawater.
Fuel System Optimization and Care
Fuel Filter Replacement Procedures
Clean fuel delivery ensures optimal cummins engine performance and prevents injection system damage from contaminated diesel fuel. Replace primary and secondary fuel filters according to maintenance schedules, typically every 500 hours or when restriction indicators signal replacement needs. Contaminated fuel filters can cause power loss, rough operation, and potential damage to expensive injection components.
When replacing fuel filters, prime the system properly to eliminate air pockets that could cause starting difficulties or erratic operation. Inspect fuel lines and connections for leaks, corrosion, or damage that could allow air infiltration or fuel contamination. Maintain fuel tank cleanliness by draining water separators regularly and treating fuel with appropriate biocides to prevent microbial growth.
Fuel Quality Management
Fuel quality directly impacts cummins engine performance, emissions, and component longevity. Use only clean, high-quality diesel fuel that meets or exceeds manufacturer specifications for sulfur content and cetane rating. Poor fuel quality can cause injection system damage, increased emissions, and reduced engine life expectancy.
Store fuel properly to prevent water contamination and microbial growth that can clog filters and damage injection components. Consider fuel testing for critical applications to verify quality before use. In marine environments, pay special attention to fuel tank ventilation and water separation to prevent contamination from condensation and wave action.
Electrical System Maintenance
Battery and Charging System Care
Reliable electrical system operation ensures consistent cummins engine starting and proper control system function. Maintain battery terminals clean and tight, applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion that could cause starting failures. Check battery electrolyte levels regularly in serviceable batteries and maintain proper charge levels through regular operation or external charging when necessary.
Test charging system output regularly to ensure alternators maintain proper battery charge and support electrical loads during operation. Faulty charging systems can lead to battery failures and potential engine shutdown in critical applications. Inspect wiring harnesses for damage, corrosion, or loose connections that could cause electrical faults or sensor malfunctions.
Control System and Sensor Maintenance
Modern cummins engines incorporate sophisticated electronic control systems that monitor and optimize engine performance. Keep sensor connections clean and secure to ensure accurate readings and proper engine operation. Contaminated or damaged sensors can trigger fault codes, reduce performance, or activate protective shutdowns.
Regularly download and analyze diagnostic data to identify developing issues before they cause failures. Many control systems provide predictive maintenance alerts based on operating parameters and accumulated wear indicators. Address fault codes promptly to prevent minor issues from developing into major repairs requiring extended downtime.
Preventive Maintenance Planning
Maintenance Scheduling and Record Keeping
Developing and following a comprehensive maintenance schedule ensures all cummins engine systems receive proper attention at appropriate intervals. Create detailed maintenance logs that track service dates, parts replaced, and any observations or concerns noted during inspections. Consistent record keeping helps identify patterns and predict future maintenance needs while supporting warranty claims when necessary.
Plan maintenance activities around operational requirements to minimize downtime impact on productivity. Stock critical spare parts and filters to avoid delays when maintenance becomes due. Consider seasonal maintenance schedules that address specific requirements for different operating conditions or storage periods.
Training and Safety Considerations
Ensure maintenance personnel receive proper training on cummins engine service procedures and safety requirements. Improper maintenance techniques can cause damage or create safety hazards during operation. Follow lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance work and use appropriate personal protective equipment to prevent injuries.
Stay current with manufacturer service bulletins and technical updates that may affect maintenance procedures or intervals. Participate in factory training programs when available to maintain expertise on evolving engine technologies and service techniques. Proper training investment pays dividends through improved maintenance quality and reduced repair costs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Performance Problem Diagnosis
Understanding common cummins engine performance issues helps identify problems early and prevent more serious damage. Power loss symptoms often indicate fuel system restrictions, air intake problems, or turbocharger malfunctions requiring systematic diagnosis to identify root causes. Monitor operating parameters regularly to establish baseline performance metrics for comparison when problems develop.
Excessive smoke production typically indicates combustion problems related to fuel injection, air intake, or internal engine wear. White smoke often suggests coolant leaks into cylinders, while black smoke indicates incomplete combustion from fuel or air delivery issues. Address smoke problems promptly as they often indicate developing issues that will worsen without intervention.
Noise and Vibration Analysis
Unusual engine noises or vibrations can indicate developing mechanical problems requiring immediate attention. Bearing knock, valve noise, or injection system clatter suggests internal wear or damage that could lead to catastrophic failure if ignored. Establish baseline noise characteristics during normal operation to help identify changes that warrant investigation.
Vibration issues may indicate engine mount problems, internal imbalance, or drivetrain misalignment affecting both performance and component longevity. Use vibration analysis tools when available to quantify changes and track developing problems over time. Address unusual noises or vibrations promptly to prevent minor issues from escalating into major repairs.
FAQ
How often should I change the oil in my cummins engine
Oil change intervals for cummins engines typically range from 250 to 500 hours of operation, depending on your specific engine model and operating conditions. Severe duty applications such as marine use, dusty environments, or frequent short trips may require more frequent oil changes. Always consult your engine manual for manufacturer-recommended intervals and use only approved oil specifications to maintain warranty coverage and optimal performance.
What type of coolant should I use in my cummins engine
Use only coolants that meet cummins specifications, typically requiring ethylene glycol-based antifreeze mixed with distilled water in a 50/50 ratio. The coolant must provide adequate freeze protection for your climate while containing proper corrosion inhibitors to protect internal engine components. Avoid mixing different coolant types and replace coolant according to maintenance schedules to maintain protection effectiveness throughout the service interval.
How can I tell if my air filter needs replacement
Check air filter condition every 100 hours of operation or when restriction indicators reach specified limits. Visual inspection should reveal minimal contamination, while excessive dirt buildup or damaged filter media requires immediate replacement. Many engines include restriction gauges that indicate when filter replacement is necessary, typically when restriction reaches 15-20 inches of water column depending on engine specifications.
What are the signs of fuel system problems in cummins engines
Common fuel system problem indicators include hard starting, rough idle, power loss, excessive smoke, or engine stalling. Water contamination may cause white exhaust smoke and poor combustion, while contaminated filters can restrict fuel flow causing power reduction. Regular fuel filter replacement and proper fuel quality management prevent most fuel system issues from developing into expensive repairs requiring injection system overhaul.